"Some organisms are capable of capturing the energy from sunlight and using it to produce organic compounds. This process, known as photosynthesis, is essential to life as it provides energy for both producers and consumers. Photosynthetic organisms, also known as photoautotrophs, are organisms that are capable of photosynthesis. Some of these organisms include higher plants, some protists (algae and euglena), and bacteria." (https://www.thoughtco.com/all-about-photosynthetic-organisms-4038227)
Algae
Pinnularia
Classification
- Domain: Eukaryota
- Phylum: Heterokontophyta
- Class: Bacillariophyceae
- Genus: Pinnularia
Description
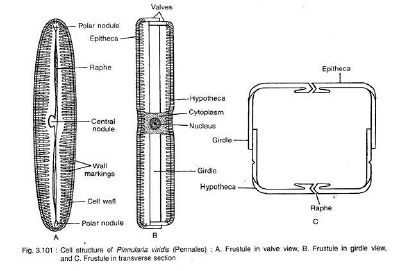
Pinnularia is a fresh water alga, a type of diatom (phytoplankton/Bacillariophyceae) which is lives in oceans, in fresh water, in soils, and on damp surfaces. “Diatoms are unicellular, although they can form colonies in the shape of filaments or ribbons (e.g. Fragilaria), fans (e.g. Meridion), zigzags (e.g. Tabellaria), or stars (e.g. Asterionella).” “Diatoms generally range in size from 2 to 200μm” (wikipedia)
“A unique feature of diatom cells is that they are enclosed within a cell wall made of silica (hydrated silicon dioxide) called a frustule.” “The cell itself consists of two halves, each containing an essentially flat plate, or valve and marginal connecting, or girdle band.” “Although the shape of the cell is typically circular, some cells may be triangular, square, or elliptical.” (wikipedia)
“Only male gametes of centric diatoms are capable of movement by means of flagella.” (wikipedia)
“A feature of diatoms is the urea cycle, which links them evolutionarily to animals.” (wikipedia)
“Reproduction among diatoms is primarily asexual by binary fission, with each daughter cell receiving one of the parent cell's two frustules (or theca).” “Pinnularia like most diatoms, can reproduce by simple cell division. Nuclear division occurs by mitosis and cell divides into two parts. Each daughter receives one of the parent cell's thecae, which becomes that cell's epitheca. The cell then synthesizes a new hypotheca. Thus one daughter is the same size as the parent, and one is slightly smaller.” (wikipedia)
“Pinnularia is a predominantly fresh-water alga, usually found in ponds and moist soil. They can also be found in springs, estuaries, sediments, and oceans. Members of this genus are most commonly found in 40 cm of water, at 5 °C.” (wikipedia) “Pinnularia are elongated elliptical unicellular organisms.” “Their walls are composed of two halves called thecae (or less formally, valves.)” (wikipedia)
Medium
bacteria
Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis)
Classification
- Domain: Bacteria
- Phylum: Cyanobacteria
- Genus: Spirulina
Description
“Cyanobacteria is a phylum of bacteria that obtain their energy through photosynthesis” “Cyanobacteria used to be called blue-green algae but they are prokaryotes and the term "algae" in modern usage refers to eukaryotes.” (wikipedia)
“As prokaryotes, cyanobacteria do not have nuclei or an internal membrane system.“ “Photosynthesis is performed in distinctive folds in the outer membrane of the cell (unlike green plants which use organelles adapted for this specific role, called chloroplasts). Biologists commonly agree that chloroplasts found in eukaryotes have their ancestry in cyanobacteria, via a process called endosymbiosis.” (wikipedia)
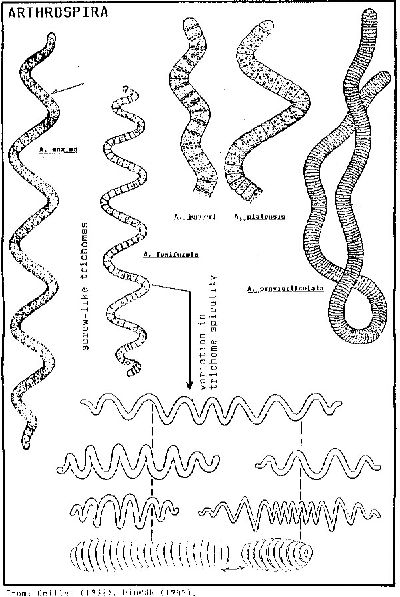
“Cyanobacteria are arguably the most successful group of microorganisms on earth. They are the most genetically diverse; they occupy a broad range of habitats across all latitudes, widespread in freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems, and they are found in the most extreme niches such as hot springs, salt works, and hypersaline bays.”(Stewart I and Falconer IR (2008) "Cyanobacteria and cyanobacterial toxins" Pages 271–296) “Cyanobacteria prefer calm waters, such as those provided by ponds and lakes.” “They may be free-living or form symbiotic relationships with plants or with lichen-forming fungi” “They range from unicellular to filamentous and include colonial species.” (wikipedia)
“Each individual cell of a cyanobacterium typically has a thick, gelatinous cell wall. They lack flagella, but hormogonia of some species can move about by gliding along surfaces. Many of the multicellular filamentous forms of Oscillatoria are capable of a waving motion; the filament oscillates back and forth. “ (wikipedia)
“The optimal growth temperature for A. platensis is 35 – 38 °C. This poses a major limiting factor outside the tropics, confining growth to the summer months.[22] A. platensis has been grown in fresh water, as well as in brackish water and sea water.” (wikipedia)
Medium
"The water need to be pure for the reasons we just explained. This doesn’t mean that you have to use bottle water but you should filter the tap water – something like a Brita filter will do just fine." "If you use river water, use UV filters in addition to active carbon filter(the Brita type), as you might have other algae or organisms in the water that could compete or eat spirulina."(http://www.spirulinaacademy.com/how-to-grow-your-own-spirulina-at-home-the-culture-medium/)
"Spirulina requires relatively high pH values between 9.5 and 9.8 ( Belkin and Boussiba, 1971)"
Protists
Euglena
Classification
- Domain: Eukaryota
- Class: Euglenoidea
- Genus: Euglena
Description
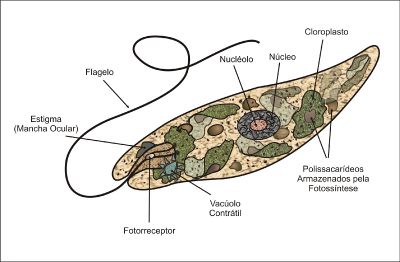
Euglena is a (endo)symbiotic creature. It is also considered belonging to protista kingdom, having features of animal, plant or fungus.
“Euglena are found in fresh and salt waters. They are often abundant in quiet inland waters where they may bloom in numbers sufficient to color the surface of ponds and ditches green (E. viridis) or red (E. sanguinea).” (wikipedia)
“Most species of Euglena have photosynthesizing chloroplasts within the body of the cell, which enable them to feed by autotrophy, like plants. However, they can also take nourishment heterotrophically, like animals.” (wikipedia)
Medium
"Combine 1 L of spring water or Chalkley’s 1x solution or Pringsheim’s, 20 wheat or rice grains, and 5 mL (1 tsp) of dry powdered milk in a beaker. Boil the mixture for 5–10 minutes, and then dilute this mixture with 3 L of spring water. Let this solution cool and stand uncovered for 24 hours." "Shake or stir the media solution and fill shallow containers with wide bottoms approximately half full. (Stacking culture bowls work best.) Add 50–100 mL of Euglena stock culture to each bowl. The Euglena culture medium contains a great deal of organic matter. Bacteria will grow rapidly and the cultures are likely to have a pungent odor for several days. (Take this into consideration when selecting a culture storage location.)"
Chalkley’s Stock Solution 10x (Dilute by a factor of 10 for 1x (e.g., dilute 100 mL to 1 L with distilled water))
0.06 g CaCl2 1.00 g NaCl 0.04 g KCl 1 L Distilled water
Autotrophic/mixotrophic euglena medium: https://www.uni-weimar.de/kunst-und-gestaltung/wiki/File:Euglenamedien.pdf
More info: File:Culturing-Euglena.pdf