| (76 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
This page documents my work and experiments done during the "Max and I, Max and Me" course. Feel free to copy, but give attribution where appropriate. | This page documents my work and experiments done during the "Max and I, Max and Me" course. Feel free to copy, but give attribution where appropriate. | ||
= | = ISS overhead = | ||
[[File:ISS_overhead.png|400px]] | |||
[[File:people_in_space.mp3]] | |||
The International Space Station is currently the only extraterrestrial habitat for humans. It circles the earth approximately every 90 minutes and thus can look down on a vast planet. Humans on the other hand rarely look up and grasp what we accomplished and what we can reach for. This small installation tracks the International Space Station and emits a notification if it is above the place of exhibition. A handbell is rung and the names of the people currently in outer space are read out loud. | |||
The technical setup consists of a computer running Max and some means of notification like a bell or a speaker. The current position of the International Space Station is calculated from its orbital data and set into relation to the place of exhibition (e.g. Weimar). If the ISS is at a place which can be considered overhead the notification is triggered. | |||
[[ | = implementation notes = | ||
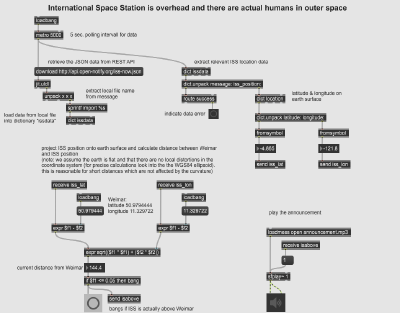
The underlying Max patch for tracking the ISS and playing audio looks like this: | |||
[[File:ISS_overhead_patch.png|400px]] | |||
[[File:ISS_overhead_2021-06-14.maxpat|Max patch]] | |||
[[ | Processing TLE files and orbital data was sidestepped by relying on [http://open-notify.org/Open-Notify-API/ISS-Location-Now/ open-notify.org] and processing [https://json.org/ JSON] data. The distance (on earth) to the city center of Weimar (at 50.979444, 11.329722) calculated using the euclidian distance as a metric. To simplify the math it is assumed that the world is flat and the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_Geodetic_System#WGS84 WGS 84] reference system is ignored. This is ok for small distances where the curvature of the earth does not result in too much of an error. | ||
The Max patch was [https://docs.cycling74.com/max8/vignettes/standalone_building exported to a standalone application]. It is now run on a small computer board to reduce the complexity of the setup. The data about the ISS crew is scraped from the internet using custom written software. | |||
Lessons learned: | |||
* sometimes you can find an API for exactly the data you need | |||
* occasionally ignoring the material reality is feasible on very narrow bounds | |||
* school math turned out to be useful | |||
= references = | |||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_Space_Station wikipedia: International Space Station] | |||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Two-line_element_set wikipedia: two-line element set (TLE)] | |||
* [https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/SpacecraftQuery.jsp NASA Space Science Data Coordinated Archive Master Catalog Search] | |||
* [https://www.howmanypeopleareinspacerightnow.com/ how many people are in space right now?] | |||
* [[Max and I, Max and Me class notebook]] | |||
* [https:// | |||
* [https:// | |||
* [https:// | |||
* [https:// | |||
* [ | |||
Latest revision as of 13:11, 17 June 2021
This page documents my work and experiments done during the "Max and I, Max and Me" course. Feel free to copy, but give attribution where appropriate.
ISS overhead
The International Space Station is currently the only extraterrestrial habitat for humans. It circles the earth approximately every 90 minutes and thus can look down on a vast planet. Humans on the other hand rarely look up and grasp what we accomplished and what we can reach for. This small installation tracks the International Space Station and emits a notification if it is above the place of exhibition. A handbell is rung and the names of the people currently in outer space are read out loud.
The technical setup consists of a computer running Max and some means of notification like a bell or a speaker. The current position of the International Space Station is calculated from its orbital data and set into relation to the place of exhibition (e.g. Weimar). If the ISS is at a place which can be considered overhead the notification is triggered.
implementation notes
The underlying Max patch for tracking the ISS and playing audio looks like this:
File:ISS overhead 2021-06-14.maxpat
Processing TLE files and orbital data was sidestepped by relying on open-notify.org and processing JSON data. The distance (on earth) to the city center of Weimar (at 50.979444, 11.329722) calculated using the euclidian distance as a metric. To simplify the math it is assumed that the world is flat and the WGS 84 reference system is ignored. This is ok for small distances where the curvature of the earth does not result in too much of an error.
The Max patch was exported to a standalone application. It is now run on a small computer board to reduce the complexity of the setup. The data about the ISS crew is scraped from the internet using custom written software.
Lessons learned:
- sometimes you can find an API for exactly the data you need
- occasionally ignoring the material reality is feasible on very narrow bounds
- school math turned out to be useful
