| Line 172: | Line 172: | ||
When you do interviews there are some common problems that can occur. | When you do interviews there are some common problems that can occur. | ||
# '''You ask "yes/no" Questions''' <br> | # '''You ask "yes/no" Questions''' <br>You: ''"Do you like this mobile phone?"'' Interviewee ''"Yes!"''<br>What do we know now? Nothing.<br>Solution:''"What do you like about the phone?"''<br><br> | ||
You: ''"Do you like this mobile phone?"'' Interviewee ''"Yes!"''<br> | #'''The Interviewee answers in very abstract ways'''<br>Interviewee answer: '''"In general these things make me think about..."''' <br>The answer does not tell us something interesting about the real life of the user. <br>Solution:''"Can you tell me about the situation it happened the last time?"''<br><br> | ||
What do we know now? Nothing.<br> | #'''The Interviewee demands a specific feature'''<br>Interviewee answer: '''"Well... You just need to put a red button here!"''' <br>Users don't know what would make a design that is good to use for everybody. We dont know either for sure, so we do research!<br>Solution:''"How would the red button help you?"''<br><br> | ||
Solution:''"What do you like about the phone?"'' | #'''You want to know if a feature you have in mind would be good'''<br>You: '''"Would it help you to have a green lever that does [whatsoever]?"'''<br>This is similar to the situation above. What the user understands will be just "...help you?" or "...feature..." so help and features are considered as good so the answer will be ''"yes"''!<br>Solution:Don't ask this question! It would be more useful to gather informations about the user and his/her context that could reveal if the user needs the feature that you have in mind. | ||
#'''The Interviewee answers in very abstract ways'''<br> | |||
Interviewee answer: '''"In general these things make me think about..."''' <br> | |||
The answer does not tell us something interesting about the real life of the user. <br> | |||
Solution:''"Can you tell me about the situation it happened the last time?"'' | |||
#'''The Interviewee demands a specific feature'''<br> | |||
Interviewee answer: '''"Well... You just need to put a red button here!"''' <br> | |||
Users don't know what would make a design that is good to use for everybody. We dont know either for sure, so we do research!<br> | |||
Solution:''"How would the red button help you?"'' | |||
#'''You want to know if a feature you have in mind would be good'''<br> | |||
You: '''"Would it help you to have a green lever that does [whatsoever]?"''' <br> | |||
This is similar to the situation above. What the user understands will be just "...help you?" or "...feature..." so help and features are considered as good so the answer will be ''"yes"''!<br> | |||
Solution:Don't ask this question! It would be more useful to gather informations about the user and his/her context that could reveal if the user needs the feature that you have in mind | |||
==Conducting Interviews== | ==Conducting Interviews== | ||
Revision as of 21:02, 6 October 2010
A Students Guide to Interaction Design Solltest ihr irgendwetas ändern: bitte beachtet, dass eure Beiträge unter Creative Commons Lizenz stehen werden. If you change something, please note that this work and you edits are licensed under a Creative Commons
Licence: This work is licenced under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported.
Preface
goals: This guide is aimed at students who want to develop new products, services, software or websites. We cover the whole interaction design process in a brief and understandable way and enable students to understand the most important terms so that they can read the literature.
No-Goals: Include material that is non-relevant for practical work.
Foundations
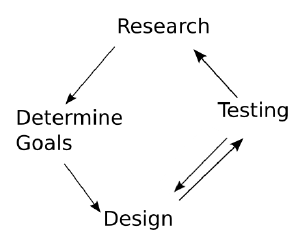
Iterative Design Process
The iterative design process helps you to structure your design process. It is an easy to use cycle model, which steps you can follow. The Process of doing so is explained in this guide.
The steps are:
- Research: in which you gather informations about user goals, existing problems and already existing solutions.
- Formulating you goals: Helps you to know what you actually want to archive with your design (and what not!). This can be seen as belonging to research but it is crucial to make the research useful, so it's got its own bullet-point!
- Design: Is creating solutions for what you want to archive. You start with a broad design of that is fairly abstract and make your ideas more concrete over time.
- Testing: After you designed you need to test if your ideas work as you expected. This is can be a hard thing to do because some things that seem to be great turn out to be unsuitable for your users. Otherwise you will get all sorts of interesting insights that will help you in improving your ideas.
The model is called iterative because you will go through the all or a part of the steps several time. Doing all steps one after the other one time is known as an "iteration". Each time you do so, you improve your product and former abstract things will become more concrete.
The model can be applied for designing the general product as well as for designing a small feature. You don't need to do all steps each time you try to solve a problem. It is very common to design, test and refine the design based on the test's results to test again. But you should at least consider the possibility to research.
So what is all that good for? Following the steps helps you to understand your users by doing research. So you don't design for non-existing needs or interfaces nobody can use. It helps as well to be more creative at the end: by dealing with your users, you will see your designs from a new perspective and so develop new ideas.
A small Example
Imagine you design a new mobile phone. You can use the process that is suggested here to design the general product: You will research how people will use the phone, you will determine which features you need for meeting the users needs. Than you will design how all features work together in the phone and how it will look like. At the end you test it.
During this process you will see that you need to answer smaller questions like how to implement sending messages: Is it better to have different facilities for SMS, MMS and e-mail, or shall they be combined in one view so that the user can ignore the differences between the different techniques?
For getting to know how to deal with this you can again use the cycle model:
1) Find out how the users think about messages and how they use them.
You may find out that users think of their messages all in the same way when they get them but in technical terms when they write them
2) Write down what you need to keep in mind when you design
I want to design a unified view for incoming messages while still providing explicit control over self initiated or reply-messages
3)Than you design...
4)...and test.
Example:It turns out that your design was overall easy to use but that some users had trouble with selecting the message type while sending
What you do now is trying out different ways to make the type-selection easier, so you just repeat the "mini-cycle" of testing and design.
Usability Goals
The usability goals are a collection of the very basic user needs. They are broad, but you will have no trouble to understand them.
Utility
If your product's functionality matches the needs of your users and enables them to reach their goals it has a good utility.
You can find out your users needs and goals by doing "user research" which means that you apply some research methods. One of these methods is doing a special kind of interview with some users. I will cover this technique in a latter chapter.
Learnability
A good learnability exists if the users you target can use your product without putting a lot of effort learning. This is especially important for the very basic functions.
Ideally users don't have to bother about new concepts and unknown terms.
Learnability is what will be the first thing that comes into your mind if you think about interaction design. Paradoxically it is a principle that is ignored in many products: Industry often uses a lot of functions that diminish learnability and many student projects ignore learnablity and focus on efficiency. You can improve the learnability of your application by learning common principles of design like "visibility" or "consistency" and by testing your ideas with your users. Material for learning this will be provided in latter chapters.
Efficiency
Your product has a good efficiency if the user can archive a high productivity. This simply means he/she can do more in less time once it is known how one uses the product. Efficiency can be archived with optimizing the ways the functions are accessed and with providing additional ways of interaction like keyboard shortcuts. Efficiency is important, but in my experience it is easiely over-emphasized as one does not need to learn one's own designs and efficient stuff feels just great. But a command line interfaces or gestural interaction are cool and really efficient if you can use it but they need to be explicitly learned before they can be used. And the difficulties of learning are often underestimated by interaction design beginners.
Safety
Safety is protecting the user and his/her creations from undesired outcomes. Very basic is that you provide a product that does not crash and destroys the users data by doing so.
You should as well prevent that the user selects data-destroying functions by accident. E.g. putting the "save" and the "close" entry close to each other in a menu will cause data loss: if the user wants to save, he may press "no" after a dialog window appears: "don't bother me now. I want to save my data!" - and the data is lost, "close" was selected by accident and the dialog-window that was dismissed by choosing "no" was the final warning.
Even if you prevent accidental actions the users data is not save. Users may misunderstand the name of an action or just try out what the result will look like. Therefore you should provide an undo-facility. This means the user can do an action and if it turns out that this has been a bad idea it can be undone. This is a great feature that demands a bit of thinking when the code is written but it is worth it. As a side effect your application becomes more learnable as well: users are able to learn by doing without any worries.
Simplicity
When I say simplicity I do neither mean "ease of use" nor "looking shiny and smooth". The kind of simplity I mean in this chapter is implementing only the features that are important for your idea and to implement them in a way that they work together greatly. You should not add anything because it is a nice to have or one in ten people thought it would be useful. Every time you add a feature, you need to make it fit to the rest of your product. It potentially will make it slower, less solid and more difficult to use. And keep in mind: the ressources you use to add features (you are probably student so it is: time) can't be used for refining the really crucial features.
So how do you decide which features you are going to implement?
I don't have any instant solution. The most important is that you keep in mind that you should create a unique, easy-to use product that does do what it does greatly. During this course you will learn how to do user research to find out about the goals and problems of your users. Try to find out what really matters for all of them. If you see that you have two different groups of people, find out if they are similar enough to serve them one product. If they differ too much, say goodbye to one of them and design just for one of the groups - maybe you come back later to the other, but first concentrate on one thing.
But what about the products that are used by everyone? In case you want to design something like this you should not apply the suggestions above, right? Well, when I think about products for everybody I think of facebook for example. It has a vast number of users so this is enough "everybody" for a beginning interaction designer I think. Though strangely, Facebook started with a very restricted target group: Students of the Harvard University. Slowly and controlled it was opened to more people. First Students of other elite US universities ("Ivy League"). Than all other US universities. Than Highschool students, employees of several big companys and finally it was open for everybody. I don't want to put them on a pedestal for great interaction design. I just want to illustrate that they are successful and did not "desgin for everybody".
What this illustrates as well is that it is always easier to add features. Removing them if you note that they don't help you is very hard. You can do so but nobody likes it. What if a function that you particularly use would disappears after an upgrade of your favourite software?
If you release a successful 1.0 Product you can still extend it in the 2.0 version even with features that are not very-super-crucial. But I write this to help you to release a successful 1.0 version so I did put emphasis on the simplicity.
Research
The research is the preperation for the actual design process. Doing research will help you to design for what the users want to archive and to avoid common problems. It is also likely that some other people did work you can build on. This can save you a lot of time and pondering.
It is usefuil to do research on
- Your users goals (what they want to archive)
- Existing Problems
- Solutions, Experiences and Problems others had in similar projects.
not to underestimate is:
- Getting inspiration
You may think that it is not necessary to do research as you are a clever person who knows already a good bunch of stuff about what you design for. Cognitve Psychologist and UX Professional Don Norman rightly says: "we tend to project our own rationalisations and beliefs onto the actions and beliefs of others". In other words:You think others are like you. But the interesting thing is: they are not the same. So you need to find out via research.
In the beginning of your Project the main research activity will be doing user research and getting to know the goals and problems of your users. Later on you will probably solve more specific problems and use more books and online ressources to solve these problems.
It is important to get to know what your users what to archive – what their goals are. Goals are not activities like using a feature in your product. "Finding that funny picture from the last holiday" is a goal the user might have, searching for it is not a goal the user has. If search would not be needed to find the picture she would not search!
Use what is already out there
The easiest (though least exiting) way to get insights is researching for ressources you can use. Using existing ressources is useful in later project stages when you need to solve specific problems and already know about your users goals.
If the topic you want to work on is new for you it might be a good start to start with a book that offers an overview on the field of interest. It will help you as well to get to know the special terms that are used in a more specialized topic. This can be crucial: I often searched for papers of otehr ressources on the web. What often took the most itme was getting to know the name of what I was actually looking for. For a recent project on online collaboration in design I googled a lot about "Open Design", Collaborative Design" etc. finally I found out, that the term that gave me some interesting links was "open source design" – which was not what I would have guessed initially.
This leads us to the very common possibility to use a search engine to find interesting sites on your topic. The UX community blogs a lot and there is a lot of stuff out there.
In case you have a specific problem you can consider scientific papers. If you need an answer on questions like "what do people remember about their documents?" or "is bimanual interaction an advantage for navigating in virtural space?" than you should go for science!
Reading papers may feel difficult whan you start and often they contain graphs and numbers that tell you nothing at the first moment. But you will see that they all follow a common structure so after you got this you will easily find the parts that are of an interest for you - kost likely the introduction telling waht the paper is about and the conclusions about what they found out.
Waht is especilly cool about scientific papers is that the authors quote other authors findings and that the paper is again quoted by other researchers. So everything is connected – and once you found a paper that you like and find useful you get connections to all sorts of related papers.
You can search for papers by using google scholar or the ACM Library. The search is free in both cases but just google scholar links sometimes directly to the papers while you need a membership for ACM. If your university has one, you are a lucky student! But even if you find a paper on ACM or google scholar links on a pricy database too you should give it a try and search specifically for that papers title. Often the researchers have published accessible versions on their webpages.
Interviews
A very useful tool for doing research are interviews. They are not difficult to do, very versatile and you will get a lot of insight.
You want to interview potential users of your product, so you need to see who could use your product. Than you try to get these people to an interview. You can use a couple of ways to contact these potential users: Use your universities Mailing List, ask friends of friends. As you can do the interviews via skype as well, you can state that you search for interviewees on your twitter-page or blog. (Remember: you don't search for everybody, so state for which people you are looking for) As a student you have probably mo money you can offer as compensation. So at least you should offer some coffee and cookies to your interviewees!
The important thig about the interview is that you don't ask specific and direct questions but open ones. So the answers you should aming for are not "yes" or "no" but e.g. the ones the user can tell you experiences or explaines you something. Often it will be usefull to follow up something the user said. Asking why a decision was made in a specific way or how something works can reveal important facts.
Here are some open Questions as an example
- What motivates you to do this?
- What was the best day at work in the last weeks? (Follow up with "why?")
- What annoys you when you work on this?
When you do interviews there are some common problems that can occur.
- You ask "yes/no" Questions
You: "Do you like this mobile phone?" Interviewee "Yes!"
What do we know now? Nothing.
Solution:"What do you like about the phone?" - The Interviewee answers in very abstract ways
Interviewee answer: "In general these things make me think about..."
The answer does not tell us something interesting about the real life of the user.
Solution:"Can you tell me about the situation it happened the last time?" - The Interviewee demands a specific feature
Interviewee answer: "Well... You just need to put a red button here!"
Users don't know what would make a design that is good to use for everybody. We dont know either for sure, so we do research!
Solution:"How would the red button help you?" - You want to know if a feature you have in mind would be good
You: "Would it help you to have a green lever that does [whatsoever]?"
This is similar to the situation above. What the user understands will be just "...help you?" or "...feature..." so help and features are considered as good so the answer will be "yes"!
Solution:Don't ask this question! It would be more useful to gather informations about the user and his/her context that could reveal if the user needs the feature that you have in mind.