Tobiaszimmer (talk | contribs) |
Tobiaszimmer (talk | contribs) (→Code) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
»10^-300« was written in [https://threejs.org/ three.js], using the physics library [https://github.com/lo-th/Oimo.js/ oimo.js]. | »10^-300« was written in [https://threejs.org/ three.js], using the physics library [https://github.com/lo-th/Oimo.js/ oimo.js]. | ||
The video was rendered with [https://github.com/spite/ccapture.js/ CCapture.js], "a library to help capturing animations created with HTML5 canvas at a fixed framerate". | |||
Revision as of 21:44, 21 May 2017
Final Project
10^-300
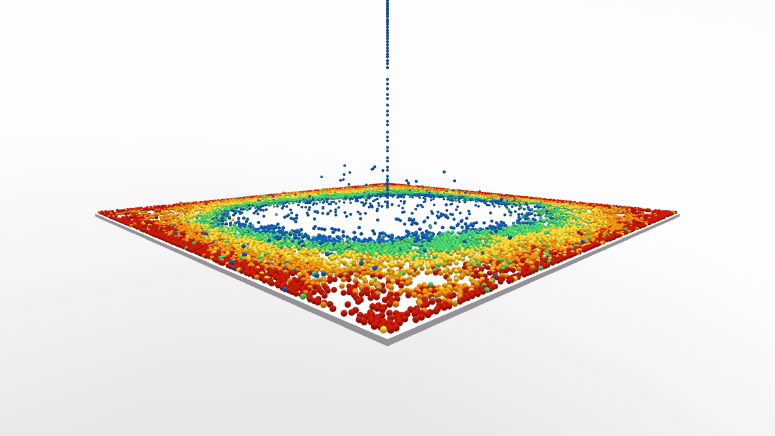
»10^–300« was created as an accompanying computer simulation for the show »20.000!« at ACC-Gallery Weimar, a collaborative exhibition organized by artist Lodewjik Heylen, Martin Schneider and the students of the »Meandering through Space« class (Maud Canisius, Linda Anna-Sophia Dertinger, Rachel Smith, Tobias Zimmer). The gallery floor was filled with 20.000 ball pit balls, ordered by color before the opening and subsequently brought into chaos by entering visitors. The balls mix slowly, create patterns, formations and sequences. The original structure falls apart into visual chaos, resulting in a fluid stream of color.
»10^-300«, as well as the other created digital simulations included in the exhibition, establish a theoretical parallel to the tangible installation and demonstrate both correlations and absurdities in the gap between the virtual and the analog. Dropping 20.000 balls onto a digital plane, one by one, in exactly the same position, will result in a perfectly balanced stack. However, the smallest perturbation — an offset of an enormously tiny magnitude (10^-300) — eventually has considerable impact and results in the collapse of the stack.
Click here to watch the video loop (07:21min)
Code
»10^-300« was written in three.js, using the physics library oimo.js.
The video was rendered with CCapture.js, "a library to help capturing animations created with HTML5 canvas at a fixed framerate".