Object is talking
1. Introduction
1.1 anthocyanin
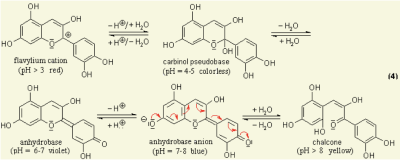
Anthocyanins are water-soluble vacuolar pigments. In the 1664 book Experiments and Considerations Touching Colours by chemist Robert Boyle, various edible plants are reported as visual pH indicators due to pH-responsive mechanisms in their tissues [1]. Anthocyanin is a kind of natural colorant in food and beverage industry, and has been found to possess anti-inflammatory antioxidant properties [2]. It has also been researched for use as an indicator for packaging applications to detect spoilage in pork and fish products [3]. All tissues of vascular plants contain the flavonoid anthocyanin, a pigment that changes colour under varying pH solutions. Under different pH conditions, the hydroxyl (OH) and/or methyl ether (O-CH3) groups attached to the carbon rings (figure 1) undergo reversible structural transformations and ionizations. Restructuring a molecule changes the way it ab- sorbs light, giving rise to colour changes [4].
Figure 1 Chemical diagram of colour-changing anthocyanin pH reaction [5]
1.2 red cabbage
"Red cabbage is rich in a number of bioactive substances, including anthocycanins"[Wiczkowski, 2012]. The method of extracting anthocyanin from red cabbage is easy and convenient.
2. Idea
This work is based on a research done by MIT media lab that uses organic fluid-based molecules. The molecules anthocyanin, vanillin, chitosan are used as dopants that can sense different pH values. The output is in the form of a broad spectrum of colors, odors and shapes. Based on this, the experiment focus on color changing, using kappa-carrageenan as substrate to present the reaction in a certain form. The outcome shows chemical reactions that are in daily life unreadable and unseen. What is shown here is a new design language to create new appliances. In the exhibition, color changing can be seen both in liquid and solid statues.
3. Methodology
- Hacking
- Making red cabbage indicator
- Making pH solutions
- 3.3. Process of experiment
- 1.5%w/v kappa-carrageenan in deionized water
- 0.1% w/v anthocyanin
- What I tried before
- Idea:
- Coffee always mixed with milk and sugar. We know coffee is a kind of acid drink. When it mixed with water the pH level will change. I want make its pH readable through my experiment.
- We drink coffee, mixed milk and sugar. Many people have juicer, mixed kinds of fruits together, maybe it has a good flavour, but is it really good for your health?
- As we know, acid/basic is very important to our health and the alkaline environment is good to our health, how can we know the pH of our drinks in a safe, readable, even edible way?
- I want to use red cabbage extract solution to know pH of different drinks, I can see changes of colour directly based on the chemical reaction and though comparing with pre-testing I have done, I can know pH of drinks easily.
- Process of experiment
- '''17.1.2018'''
- However, there’s a problem which I’m not sure:
- If pH has a direct relationship with health. I read some report and paper, there is a view: alkaline body environment is good for health, but it can not be said alkaline food leads to the alkaline environment/condition, it is complex medical problem.
- And also, this is a website of Acid/Alkaline Food Chart: http://www.phmiracleliving.com/t-food-chart.aspx
- And I find some healthy medicines which are used to adjust pH, the main ingredients are moderately or highly alkaline food.
- What I will do on 17th:
- 1. test just for visual and take picture:orange/lemon/onion/green onion/potato...
- 2. help to know pH level of drinkings
- Original pH
- Mixed pH (milk/coffee/tea/gouqi/sugar)
- (And is there any pH difference belongs to temperature? hot and cold )
- Question:
- How to deal with the thing insoluble in water, for instance, oil, cosmetic...
- ----
- After the work of 17th, I decided to focus on coffee not kinds of drinks to do the experiment. Because it is hard to judge pH level with one colour measurement.
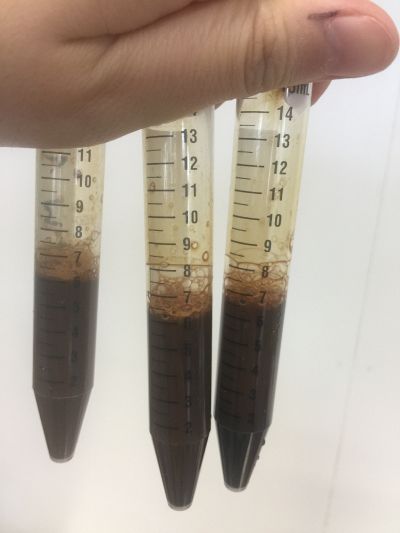
- I made 3 solutions with different proportions of red cabbage, distilled water and expresso coffee.
- 1. 5ml red cabbage solution + (1ml distilled water + 1ml coffee)
- 2. 5ml red cabbage solution + (0.5ml distilled water + 1.5ml coffee)
- 3. 5ml red cabbage solution + (1.5ml distilled water + 0.5ml coffee)
- As you can see on follow picture, the coulour results are not obvious. The
- '''19.1.2018'''
- I did the experiment of reversibility of colour change.
- And then I use reversibility of colour change to make the colour of coffee more obviously.
- PH of expresso coffee is around 6, I add the solution (pH=8) into the original solution 1/2/3, the colour changing is more obviously.
- ===4. Discussion===
- ===5. References===
- ----
- '''12.12.2017'''
- I use red cabbage to make pH indicator. The pH solution from 2 to 13.
- The red cabbage solution
after 5 minutes change to yellow
Furthur steps:
1. Rate of colour change
2. Reversibility of colour change
3. Using different pH level solutions react with the organic stuff (which has anthocyanin), see the result
However, when I change another kind of coffee and do the experiment in the same way, the colour change cannot be seen obviously. Maybe because the different ingredients of coffee.